Published: August 20, 2017
Powdery Mildew is arguable the most destructive Cannabis pest. It is an obligate biotroph that can vascularize into the plant tissue and remain invisible to a grower. It tends to emerge and sporulate 2 weeks into flowering thus destroying very mature crop with severe economic consequences. It is believed to travel in clones and its is not known if it travels in seeds. Other stressful events like cloning can trigger Powdery Mildew spore formation. While many fungicides are known to treat Powdery Mildew, many states are outlawing these fungicides due to cannabinoid extraction techniques enriching fungicides (Russo, Raber). Early detection and eradication may be the safest approach.
MacPartland et al. reported L.taurica and P.macularis as the organisms responsible for powdery mildew on cannabis. Multiple unsuccessful attempts to amplify DNA sequences from these organisms led us to whole genome shotgun sequence the Massachusetts derived organism. This sequence assembly presented a novel organism not found in NCBI.
Under ideal conditions, some powdery mildews have a 4-7 day past innoculation (dpi) window where it remains invisible as it builds a network internal to the plant (dpi work performed in arabidopsis). Research performed in a close cousin to cannabis, (Humulus lupulus or hops) has demonstrated incubation periods up to 49 days with P.macularis. The work described below was performed to test if the Cannabis derived powdery mildew vascularized network is detectable with a youPCR DNA based test prior to conidiospore generation. Later stage powdery mildew infection and conidiospore generation results in rapid spreading of the fungus to other plants. This tends to emerge and sporulate 2 weeks into flowering thus destroying very mature crop with severe economic consequences. It is believed to travel in clones and it is not known if it travels in cannabis seeds, however evidence of P.macularis transmission in Hops seeds has been reported. Detection of this pest prior to sporulation can help eradicate powdery mildew before it infests a grow with hearty spores. DNA based tools could facilitate early detection and rapid removal of infected plant materials or screening of incoming clones.
Specificity has always been our main selling point with qPCR and Aspergillus (also doesn’t grow well on petri-film) but there isn’t a single state that has PM on a list of dangerous pathogens like Aspergillus.

It remains an open debate as to the human health risks of Cannabis derived powdery mildew. While there are some anecdotal reports of allergies with PMs derived from other hosts, those allergies can’t be superimposed onto a different species. There are no states that require specific testing for these and no clinical literature supporting it as a threat to human health.
Case Studies
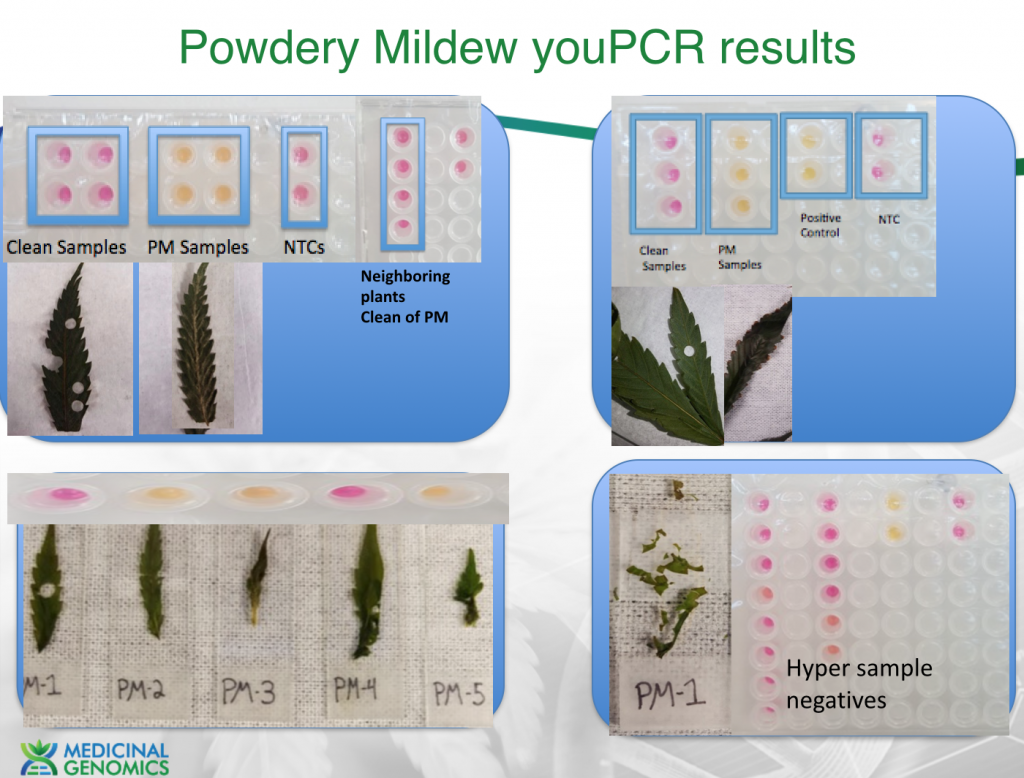
Expanded study on Powdery Mildew from CT, MA and NY
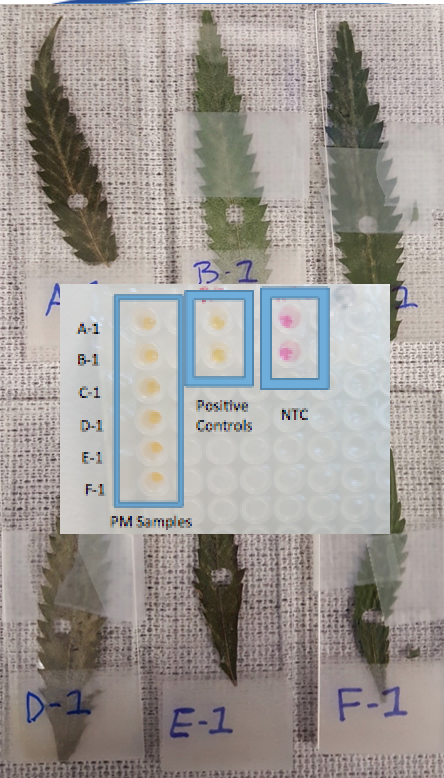

2. PCR detection vs Visual detection.-There is limited utility for a PCR test that can inform you of powdery mildews presence if you can already visibly see it. The value of a DNA based test requires an understanding of the life cycle of PM. This fungi forms a mycelium network in the plant prior to sporulation (See WeBling et al. below). Sporulation is what spreads the disease throughout a grow. This incubation period can be 7-41 days in hops. Detection and elimination of infected plants prior to sporulation can prevent the spread of the disease. To address timing of detection sensitivity we tested various strains of PM that were believed to be resistant to PM, susceptible to PM, Visibly infected of PM and non-symptomatic susceptible to PM strains.
Sample Key (left to right)
All resistant strains tested negative and all infected strains tested positive. A few NonSymptomatic strains (FSD & BBx3) had heterogeneous results likely related to sampling theory. At low mycelium density multiple 4mm hole punches may be required to for the earliest detection possible. Six 10 fold dilutions on a quantitative positive control imply we can detect single genomic copies of the species suggesting lack of assay sensitivity isn’t the cause for the heterogeneous results. However mycelium density below 2 square millimeters would result in sampling error.
To explore this we hyper sampled these strains.
2-3 Hole punches will provide earlier detection. We are exploring lysing 3 hole punches in one DNA prep to maximize sensitivity of detection while reducing youPCR costs.
Many infected strains were treated with lactobacillus and re-tested positive even though they did not visibly appear to be expressing spores. This implies the lactobacillus treatment may retard Conidia (spore) formation but does not eliminate the mycelium network.
Conclusions
Early detection of vascularized cannabis derived Powdery Mildew can be accomplished before sporulation and spreading of the disease. Early detection can drastically reduce fungicide usage and ensure safer grow environments and cleaner cannabis. Earliest detection may require triplicate sampling to provide best results.
Appendix Photos
Microscopic views of the original plant with Powdery Mildew-




Next question-
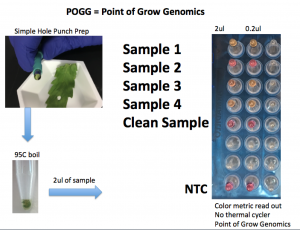
Do other parts of the plant with no visual signs of Powdery Mildew have genetic evidence of its vascularization?
Sample 1


Positive for Powdery Mildew
Sample 2


Negative for PM
Sample 3


Positive for PM
Sample 4


Positive for PM
3/4 Hole punches from microscopically clean leafs from a plant that was visually positive with powdery mildew triggered a positive results.
These results confirm previous reports of powdery mildew being heavily vascularized even if not visible by eye. This presents an opportunity to use genetic tests on Clones of a Powdery Mildew tested Mother plant. While the test costs may be $15, a few tests on a mother can significantly reduce the likelihood that the 100 clones derived from that mother contain PM. While a single clone can cost $15, one may not need to test every clone from a mother.
A single cheap clone can destroy a whole grow.
WeBling et al. Stained for Powdery Mildew. One can see the mycelium network of PM inside the leaf even if powdery mildew is not visible to the human eye. DPI = Days Post Inoculation. HPI = Hours Past Inoculation.
©2025 MEDICINAL GENOMICS CORPS
Copyright all right reserved.
Signup to receive email updates on blog posts, podcasts, webinars, new products, and more!
Join us at the CannMed 25 Innovation and Investment Summit, an exclusive experience of discovery, development, and networking with innovators from around the world.