A case of mistaken identity is causing a disagreement between two Alaska testing labs.
According to a KTUU article, state regulators gave an edible marijuana product contaminated with mold to both of the state’s testing laboratories. The labs used two different methods for microbial safety testing, which produced two different results. One used plating while the other used the PathoSEEK® Microbial Safety Testing Platform, a DNA-based method.
The lab using plating grew the mold in a culture and then viewed it under a microscope. They identified the mold to be Aspergillus niger, which is on the state’s list of prohibited microbial species, along with A. flavus, A. fumigatus, A.terreus, STEC, and Salmonella. Therefore, the lab failed the sample. However, the lab that performed DNA-based testing on the sample, did not detect DNA from any species on the state’s list.
So why did one lab see A. niger, and the other lab did not? It’s a case of mistaken identity.
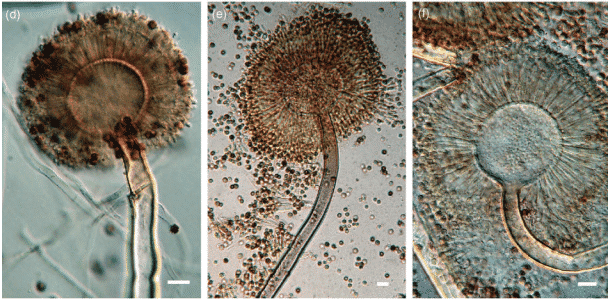
A. brasiliensis, bears a striking resemblance to A. niger, and can be easily mistaken for its more harmful relative when using sight alone. The 2007 paper that identified A. brasiliensis as a novel species noted their physical similarities. It was only when the researchers used DNA sequencing that they were able to definitively distinguish A. brasiliensis from A. niger.
Being able to correctly distinguish A. brasiliensis and A. niger is important. A. brasiliensis is not on the state’s list of dangerous microbes, and it has not been connected to any cases of Aspergillosis, the potentially deadly lung infection that can result from exposure to certain Aspergillus species. Researchers also observed that A. brasiliensis does not produce many of the compounds that are commonly produced by A. niger complex (i.e., ochratoxin A, kotanins, funalenone).
Only DNA-based testing is able to differentiate between A. brasiliensis and A. niger, and only Medicinal Genomics has DNA-based Aspergillus tests validated on cannabis. We demonstrated this in our Manufacturer’s Validation Document where we spiked A. brasiliensis into samples and it did not trigger a positive result on any of our Aspergillus detection assays. It was detected on our Total Yeast and Mold assay, as expected.
This is yet another example of why DNA-based methods are superior to culture-based methods. Identifying specific microbial strains with a microscope is like relying on eyewitness descriptions to identify a criminal. Ask any legal professional, and they will tell you eyewitness accounts are often unreliable. On the other hand, DNA evidence is often a slam dunk. Microbial testing on cannabis is no different.