Earlier this week, we made some exciting updates to Kannapedia, our public database of cannabis and hemp genetic information. We added new data visualizations and a variant table that displays Amino Acid changing SNPS in the THCA, CBDA, and CBCA synthase genes.
Read more about the updates below, and view the report for Grape Slurpy Runtz to see them in action!
CBCA Synthase Gene Coverage Visualization
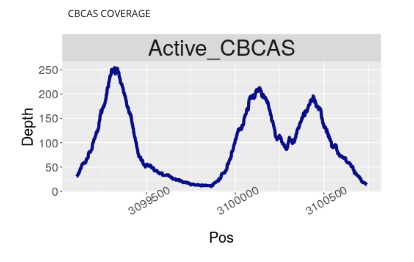
We suspect that active CBCA synthase genes may explain why some Type III plants still produce small concentrations of THCA. After all, studies have shown that when THCA, CBCA, and CBDA are cloned into yeast, fed precursor, and subjected to certain conditions, they can create different cannabinoids. Each enzyme itself is not a pure chemical reaction.
To what extent these genes are creating off-target cannabinoids in actual plants is largely unknown and likely very situational depending on the plant and the environmental conditions. To help better understand this variation we added a coverage map to each Kannapedia report.
Hopefully could be the key to helping hemp breeders and cultivators produce plants that are below the USDA’s 0.3% THCA limit.
Y-Chromosome Ratios Visualization
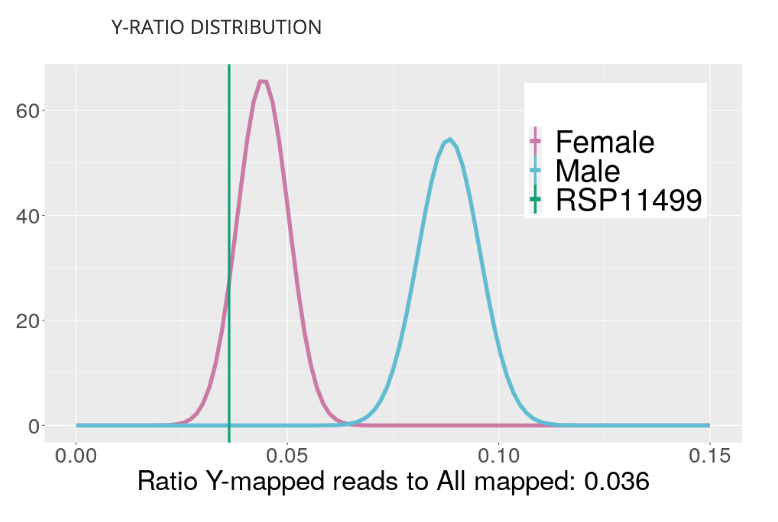
This new visualization shows the ratio of Y-chromosome loci to X-chromosome loci for all samples in the Kannapedia database that were sequenced with the same method (i.e., StrainSEEK® panel or Whole Genome). Samples that have a greater ratio of Y to X loci are males.
This method of determining sex is better than qPCR methods because it doesn’t rely on single primer set to make the call.
THCA, CBDA, and CBCA Variant Table
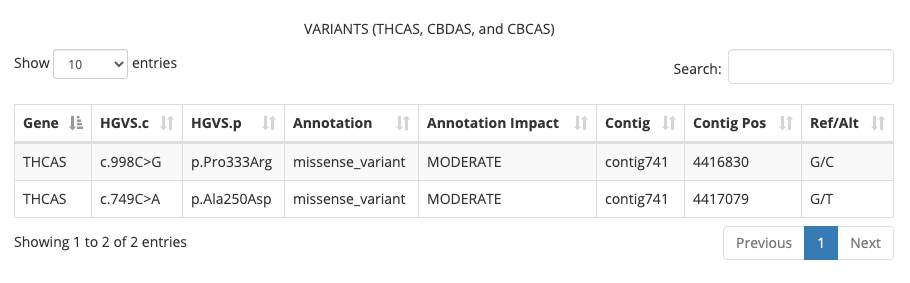
This new table displays any variants that are present within the THCA, CBDA, or CBCA synthase genes that affect the production of amino acids. So far, we have identified two types of variants:
- Synonymous coding variants are low impact changes in the sequence because they do not affect the amino acid being produced
- Missense coding variants are moderate impact changes in the sequence because they do affect the amino acid being produced
Tracking these variants will help identify SNPs that can deactivate THCA synthase or maybe alter the residual THCA being synthesized by CBDA synthase. While deletions of entire THCA synthase and CBDA synthase genes are the most common Bt:Bd alleles observed, it is possible to have plants with these genes where functional expression of the enzyme is disrupted by deactivating point mutations.
Learn more about our Genomic Services and sequence your cultivar today!